Samsung’s 3nm Chip Breakthrough: Powering the Future of Galaxy Devices and AI
Samsung has just taken a big step forward in the chip-making world by starting mass production of its 3nm chips. These tiny powerhouses promise to make next-generation Galaxy devices and AI hardware faster, more efficient, and smaller than ever. Let’s break it down and explore what this means for smartphones, smartwatches, and the booming AI industry.
What Are 3nm Chips and Why Do They Matter?
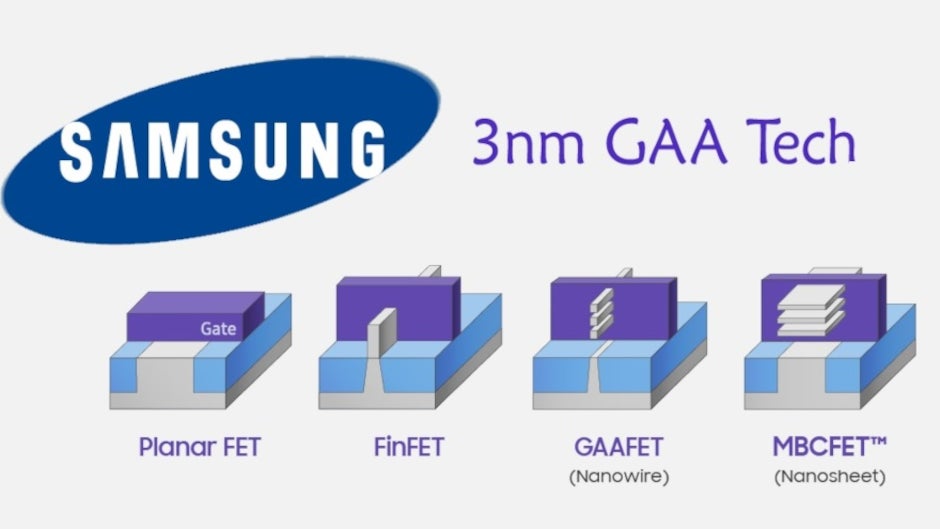
A “3nm chip” refers to a semiconductor built using a 3-nanometer process, which is a way to measure how tightly packed the chip’s components are. Smaller nanometers mean more transistors can fit in the same space, leading to better performance and lower power use. Samsung’s 3nm chips use a new technology called Gate-All-Around (GAA), which improves how electricity flows through the chip, making it more efficient than older designs like FinFET.
This milestone is a big deal because it puts Samsung ahead in the race to make smaller, more powerful chips. These chips will power everything from your next Galaxy phone to advanced AI systems in data centers. They’re designed to handle heavy tasks like gaming, multitasking, and AI processing while using less battery life.
Key Benefits of Samsung’s 3nm Chips
- Better Performance: Up to 30% faster than Samsung’s older 5nm chips, meaning apps open quicker and games run smoother.
- Energy Efficiency: Uses up to 50% less power, which could extend battery life in devices like phones and smartwatches.
- Smaller Size: Takes up 35% less space, allowing for slimmer devices or more room for other components.
Comparison of 3nm vs. 5nm Chips
| Feature | 3nm Chips (GAA) | 5nm Chips (FinFET) |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Boost | Up to 30% faster | Baseline |
| Power Efficiency | Up to 50% less power | Baseline |
| Chip Size | 35% smaller | Larger |
| Technology | Gate-All-Around (GAA) | FinFET |
Samsung’s Journey to 3nm Mass Production
Samsung kicked off mass production of its 3nm chips in mid-2022, beating its rival TSMC to the punch. However, the early days weren’t smooth sailing. The first-generation 3nm chips, known as SF3E, were mainly used for simpler tasks like cryptocurrency mining because of low production yields—basically, too many chips were coming out defective. Yields were reportedly as low as 20% in 2024, far below the 60% needed for mass production of complex chips like those in smartphones.
By mid-2024, Samsung introduced its second-generation 3nm process, called SF3, which is more refined and ready for bigger tasks. They worked with partners like Synopsys to use AI tools to fine-tune the chip design, boosting performance and yield. Now, Samsung claims their yields are stable, and they’re producing chips for high-performance devices like the Galaxy Watch 7 and possibly the upcoming Galaxy S25 series.
Challenges and Solutions
- Low Yields: Early 3nm chips had a high defect rate, making them costly to produce. Samsung used AI-driven tools to optimize designs and improve yields.
- Competition: TSMC, the world’s top chipmaker, is also working on 3nm chips. Samsung’s early adoption of GAA gives it an edge, but TSMC’s FinFET-based 3nm chips are still competitive.
- Complex Designs: Smartphone chips are much harder to make than crypto-mining chips. Samsung partnered with companies like Cadence and Siemens to streamline the design process.
Powering Next-Gen Galaxy Devices
Samsung’s 3nm chips are set to make Galaxy devices faster and more efficient. The first device to use these chips is the Exynos W1000, found in the Galaxy Watch 7 and Galaxy Watch Ultra, launched in July 2024. This chip has a five-core CPU and a Mali-G68 MP2 GPU, delivering 2.7 times faster app opening and up to 3.7 times better CPU performance compared to older models.
There’s also buzz about the Exynos 2500, which might power the Galaxy S25 series in 2025. This chip is expected to handle demanding tasks like on-device AI processing, high-resolution gaming, and 8K video recording. For example, imagine editing a video on your phone without lag or your smartwatch tracking your workouts all day without needing a charge.
Why This Matters for Galaxy Users
- Longer Battery Life: Less power-hungry chips mean your phone or watch lasts longer on a single charge.
- Faster Performance: Apps and games will load quicker, and multitasking will feel smoother.
- AI Features: More powerful chips can handle advanced AI tasks, like real-time photo editing or voice recognition, right on your device.
Boosting AI Hardware with 3nm Chips
AI is everywhere—think voice assistants, self-driving cars, or cloud servers crunching massive data sets. Samsung’s 3nm chips are built to meet these demands, especially for high-performance computing (HPC) in data centers. Companies like NVIDIA, Qualcomm, IBM, and Baidu have reportedly ordered 3nm chips from Samsung for AI-driven projects, such as GPUs for NVIDIA and AI cloud servers for Baidu.
The chips’ smaller size and better efficiency make them ideal for AI tasks that need a lot of processing power without overheating or draining too much energy. For instance, a server running AI models could process data faster while using less electricity, which is a win for both performance and the environment.
Pros and Cons for AI Applications
Pros:
- Handles complex AI algorithms with ease.
- Reduces energy costs for data centers.
- Smaller chips allow for more compact AI hardware designs.
Cons:
- High production costs due to low initial yields.
- Limited adoption so far, as some companies prefer TSMC’s chips.
What’s Next for Samsung’s Chip Technology?
Samsung isn’t stopping at 3nm. They’re already working on 2nm chips, set for mass production in late 2025. These will use an even more advanced version of GAA technology, promising up to 50% better performance and a 50% smaller chip size compared to 5nm. Samsung is also exploring 3D chip stacking, which layers chips to boost performance without increasing size—think of it like building a skyscraper instead of a sprawling house.
They’re also investing heavily in new factories, like a $10 billion plant in Taylor, Texas, to ramp up production. However, Samsung faces stiff competition from TSMC, which is also pushing for 2nm chips and has better yields on its 3nm process. Samsung’s challenge will be to keep improving yields and convincing big clients like Apple and Qualcomm to choose their chips.
Future Outlook
- 2nm Chips in 2025: Expected to power even faster devices and AI systems.
- New Factories: More production capacity could lower costs and attract more clients.
- Competition: Samsung needs to match or beat TSMC’s yields to win major contracts.





